41 valuing zero coupon bonds
Zero Coupon Bond Value Formula - Crunch Numbers A zero-coupon bond is a type of bond that doesn't make coupon payments. This type of bond is issued with a big discount to its face value. At the time of maturity, the bondholder receives the face value of the bond, which means that the current price has to be lower than the face price. The investor's earnings come entirely from the gain on redemption because there are no coupon payments. Zero Coupon Bonds - Financial Edge Value and YTM of Zero Coupon Bonds. Bonds are valued by calculating the present value of future cash flows using an appropriate discount rate or interest rate. You can calculate the price of a bond using this formula: Price of Bond = Face value or maturity value/ (1+interest rate) years to maturity.
Zero-Coupon Bond Value | Formula, Example, Analysis, Calculator The zero-coupon bond value refers to the current value of a zero-coupon bond. This formula requires three variables: face value, interest rate and the number of years to maturity. The zero-coupon bond value is usually expressed as a monetary amount. This equation is sensitive to interest rate fluctuations.

Valuing zero coupon bonds
How to Calculate a Zero Coupon Bond Price - Double Entry Bookkeeping The zero coupon bond price is calculated as follows: n = 3 i = 7% FV = Face value of the bond = 1,000 Zero coupon bond price = FV / (1 + i) n Zero coupon bond price = 1,000 / (1 + 7%) 3 Zero coupon bond price = 816.30 (rounded to 816) Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula John is looking to purchase a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 and 5 years to maturity. The interest rate on the bond is 5% compounded annually. What price will John pay for the bond today? Price of bond = $1,000 / (1+0.05) 5 = $783.53 The price that John will pay for the bond today is $783.53. Example 2: Semi-annual Compounding E3.5. Valuing Bonds (Easy) a. A firm issues a | Chegg.com Bonds with similar risk are. Question: E3.5. Valuing Bonds (Easy) a. A firm issues a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $1,000, maturing in five years. Bonds with similar risk are currently yielding 5 percent per year. What is the value of the bond? b. A firm issues a bond with a face value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 5 percent per year ...
Valuing zero coupon bonds. Bond valuation and bond yields | P4 Advanced Financial ... The plain vanilla bond with annual coupon payments in the above example is the simpler type of bond. In addition to the plain vanilla bond, candidates – as part of their Advanced Financial Management studies and exam – are required to have knowledge of, and be able to deal with, more complicated bonds such as: bonds with coupon payments occurring more frequently than once a year ... Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Here is an example of how zero coupon bond prices can change: For example, assume that three STRIPS are quoted in the market at a yield of 6.50%. The price for STRIPS with 25 years remaining to maturity would be $202.07 per $1,000 face amount That for STRIPS with 10 years remaining to maturity would be $527.47 per $1,000 face amount The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org will likely fall. Instead of getting interest payments, with a zero you buy the bond at a discount from the face value of the bond, and are paid the face amount when the bond matures. For example, you might pay $3,500 to purchase a 20-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $10,000. After 20 years, the issuer of the bond pays you $10,000. Valuing Bonds | Boundless Accounting | | Course Hero A bond's coupon is the interest rate that the business must pay on the bond's face value. These interest payments are generally paid periodically during the bond's term, although some bonds pay all the interest it owes at the end of the period. While the coupon rate is generally a fixed amount, it can also be "indexed.
Solved 2. Valuing a Zero-Coupon Bond. Assume the following | Chegg.com Answer to Solved 2. Valuing a Zero-Coupon Bond. Assume the following Calculate the Value of a Zero-coupon Bond - Finance Train Calculate the Value of a Zero-coupon Bond. Suppose you have a pure discount bond that will pay $1,000 five years from today. The bond discount rate is 12%. ... Since there are no interim coupon payments, the value of the bond will simply be the present value of single payment at maturity. Checkout our eBooks. Zero-Coupon Bonds: Definition, Formula, Example ... - CFAJournal A zero-coupon bond can be described as a financial instrument that does not render interest. They normally trade at high discounts, and offer full face par value, at the time of maturity. The spread between the purchase price of the bond and the price that the bondholder receives at maturity is described as the profit of the bondholder ... How Do I Buy Zero Coupon Bonds? | Budgeting Money - The Nest Zero coupon bonds, sometimes called strip bonds, are bonds that do not pay a regular interest rate during the life of the bond. Instead, investors buy the bonds at a discount from their face value, for example paying $700 for a $1,000 bond. When the bond matures, the investor can redeem the bond for its full face ...
CFA 53: Introduction to Fixed-Income Valuation - Quizlet The spot curve, also known as the strip or zero curve, is the yield curve constructed from a sequence of yields-to-maturities on zero-coupon bonds. The par curve is a sequence of yields-to-maturity such that each bond is priced at par value. How Do Zero Coupon Bonds Work? - SmartAsset What Is a Zero Coupon Bond? A zero coupon bond is a type of bond that trades at a deep discount and doesn't pay interest. While some bonds start out as zero coupon bonds, others are can get transformed into them if a financial institution removes their coupons. When the bond reaches maturity, you'll get the par value (or face value) of the ... Value and Yield of a Zero-Coupon Bond | Formula & Example - XPLAIND.com The bonds were issued at a yield of 7.18%. The forecasted yield on the bonds as at 31 December 20X3 is 6.8%. Find the value of the zero-coupon bond as at 31 December 2013 and Andrews expected income for the financial year 20X3 from the bonds. Value (31 Dec 20X3) =. $1,000. = $553.17. (1 + 6.8%) 9. Value of Total Holding = 100 × $553.17 ... Zero Coupon Bond: Formula & Examples - Study.com The zero-coupon bond definition is a financial instrument that does not pay interest or payments at regular frequencies (e.g. 5% of face value yearly until maturity). Rather, zero-coupon bonds...
Zero Coupon Bond Value Calculator: Calculate Price, Yield to Maturity ... Let's say a zero coupon bond is issued for $500 and will pay $1,000 at maturity in 30 years. Divide the $1,000 by $500 gives us 2. Raise 2 to the 1/30th power and you get 1.02329. Subtract 1, and you have 0.02329, which is 2.3239%. Advantages of Zero-coupon Bonds Most bonds typically pay out a coupon every six months.
Zero-Coupon Bond Definition - Investopedia If the debtor accepts this offer, the bond will be sold to the investor at $20,991 / $25,000 = 84% of the face value. Upon maturity, the investor gains $25,000 - $20,991 = $4,009, which translates...
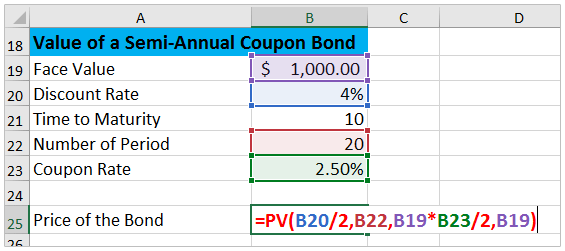
Zero Coupon Bonds Explained (With Examples) - Fervent Valuing Zero Coupon Bonds on Excel® We'll be using Excel's "PRICE" function to value Swindon Plc's bond. The first thing you want to do is setup your spreadsheet with a pro-forma / template that consists of the all different variables you'll need. The "PRICE" function on Excel® requires:
Zero Coupon Bond (Definition, Formula, Examples, Calculations) Zero-Coupon Bond Value = [$1000/ (1+0.08)^10] = $463.19 Thus the Present Value of Zero Coupon Bond with a Yield to maturity of 8% and maturing in 10 years is $463.19. The difference between the current price of the bond, i.e., $463.19, and its Face Value, i.e., $1000, is the amount of compound interest
Reserve Bank of India - Frequently Asked Questions i) Fixed Rate Bonds – These are bonds on which the coupon rate is fixed for the entire life (i.e. till maturity) of the bond. Most Government bonds in India are issued as fixed rate bonds. For example – 8.24%GS2018 was issued on April 22, 2008 for a tenor of 10 years maturing on April 22, 2018.
Zero Coupon Bond Calculator - What is the Market Value? A zero coupon bond is a bond which doesn't pay any periodic payments. Instead it has only a face value (value at maturity) and a present value (current value). The entire face value of the bond is paid out at maturity. It is also known as a deep discount bond. Benefits and Drawbacks of Zero Coupon Bonds
Net Asset Value (NAV): Formula and NAV Per Share Calculation Fixed Income Corporate Bonds Active vs Passive Investing Mutual Funds Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) Expense Ratio Municipal Bonds Commercial Paper Net Asset Value (NAV) Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS)
Zero Coupon Bond | Investor.gov Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due. The maturity dates on zero coupon bonds are usually long-term—many don't mature for ten, fifteen, or more years.
Zero-Coupon Bond: Formula and Excel Calculator - Wall Street Prep To calculate the price of a zero-coupon bond - i.e. the present value (PV) - the first step is to find the bond's future value (FV), which is most often $1,000. The next step is to add the yield-to-maturity (YTM) to one and then raise it to the power of the number of compounding periods.
14.3 Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Financial Accounting This zero-coupon bond was sold for $2,200 below face value to provide interest to the buyer. Payment will be made in two years. The straight-line method simply recognizes interest of $1,100 per year ($2,200/2 years). Figure 14.11 December 31, Years One and Two—Interest on Zero-Coupon Bond at 6 Percent Rate—Straight-Line Method
Achiever Essays - Your favorite homework help service Your writers are very professional. All my papers have always met the paper requirements 100%.
Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia General Advantages of Zero-Coupon Bonds Why would anyone want a bond without the interest? Well, for one thing, zero-coupon bonds are bought for a fraction of face value. For example, a $20,000...
PDF Numerical Example in Valuing Zero coupon Bonds - New York University For example, the value of a zero coupon bond will increase from $385.00 to $620.92 as the bond moves from 10 years to maturity to 5 years to maturity assuming interest rates remain at 10%. 4) Compare the value of the zero at 10 years to maturity when rates are 10% versus when they are 7%. Lower interest rates mean higher bond prices.
How to Buy Zero Coupon Bonds | Finance - Zacks The bonds are sold at a deep discount, and the principal plus accrued interest is paid at the bond's maturity date. The less you pay for a zero coupon bond, the higher the yield. A bond with a ...
(PDF) Sales Promotions - ResearchGate Jan 01, 2012 · Unlike direct mail, the Internet is a virtuall y zero-cost . communication vehicle. ... However, the time to clip and use th e coupon comes from the time devoted t o leisure.
E3.5. Valuing Bonds (Easy) a. A firm issues a | Chegg.com Bonds with similar risk are. Question: E3.5. Valuing Bonds (Easy) a. A firm issues a zero-coupon bond with a face value of $1,000, maturing in five years. Bonds with similar risk are currently yielding 5 percent per year. What is the value of the bond? b. A firm issues a bond with a face value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 5 percent per year ...



/97615498-56a6941c3df78cf7728f1cd4.jpg)




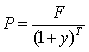



Post a Comment for "41 valuing zero coupon bonds"